Curiosity vs. FOMO: Are You Exploring or Just Scrolling?
February 26, 2026
Why Mental Health Matters for University Students
February 26, 2026Digital devices have become essential tools in our lives—but for many, they’ve also become a source of dependency. Digital addiction is a growing behavioral issue that affects people of all ages, leading to emotional, physical, and social consequences. This article explores the causes, symptoms, and solutions to digital addiction, backed by recent research and real-world examples.
What Is Digital Addiction?
Digital addiction refers to compulsive and excessive use of digital devices—smartphones, computers, gaming consoles, and social media platforms—that interferes with daily life. It shares traits with behavioral addictions such as:
- Mood modification: Using devices to escape or feel better
- Tolerance: Needing more screen time to feel satisfied
- Withdrawal: Feeling anxious or irritable when offline
- Conflict: Arguments or tension due to device use
- Relapse: Returning to excessive use after trying to cut back
While not all digital overuse is classified as addiction, the World Health Organisation has recognised Internet Gaming Disorder as a clinical condition
How Widespread Is It?
Recent global data shows that 36.7% of people are addicted to the internet, with 2.8% experiencing severe addiction. Among young adults aged 18–22, 40% report social media addiction, and the average person spends 9 hours a day on screens
In certain countries, such as the Gulf region, studies found that 30% of both parents and adolescents met the criteria for internet addiction. This is significantly higher than in countries like Italy and Greece, suggesting regional factors play a role.
Why Does It Happen?
1. Environmental and Lifestyle Factors
- Too much Hot or cold climates and limited outdoor activities lead to more indoor screen time.
- Parents often use devices to keep children occupied, unintentionally encouraging dependency.
2. Mental Health and Emotional Coping
Digital addiction can be a coping mechanism for stress, anxiety, or depression. For example, a teenager struggling with school pressure may escape into gaming or social media to avoid negative emotions
3. Family Influence
Children often mirror their parents’ behavior. If parents are constantly on their phones, children are likely to follow suit. Studies show a strong correlation between parental and child digital addiction levels
4. Tech Design Tricks
Apps use persuasive design to keep users engaged:
- Infinite scroll triggers dopamine by offering unpredictable rewards—similar to slot machines.
- Pull-to-refresh mimics gambling mechanics.
- Notifications and likes provide social validation, making it hard to disconnect.
What Are the Effects?
Digital addiction can impact:
- Sleep: 64% of teens report sleep deprivation from late-night scrolling.
- Mental health: Social media users are 3.1x more likely to experience depression.
- Physical health: “Tech neck,” eye strain, and thumb pain are common.
- Relationships: 1 in 4 couples report conflict due to “phubbing” (phone snubbing).
How Can We Address It?
🧠 Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
CBT helps individuals identify and reframe thoughts that trigger compulsive tech use. For example, someone who checks their phone every few minutes might learn to pause and ask: “What am I avoiding?”
Example: A CBT therapist might guide a client to journal their screen time triggers and replace scrolling with a walk or hobby.
📱 Digital Tools
Apps like Freedom or Forest help users limit screen time by blocking distractions or rewarding focus.
Example: Forest grows a virtual tree when you stay off your phone—if you leave the app, the tree dies. This gamifies self-control.
👨👩👧 Parental Role Modeling
Children learn by watching. Parents who set boundaries and engage in offline activities send a powerful message.
Example: A family that sets a “no phones at dinner” rule and plays board games together builds healthier habits.
🏫 School-Based Programs
Schools can implement digital media awareness programs that teach students about tech risks and self-regulation
Example: A school might run workshops where students analyze how social media apps are designed to be addictive and brainstorm healthier alternatives.
🌱 Digital Detox
Taking breaks from screens—whether for a weekend or a few hours daily—can reset habits and improve well-being.
Example: A “Tech-Free Sunday” where families go hiking or cook together without devices.
Infographic Summary
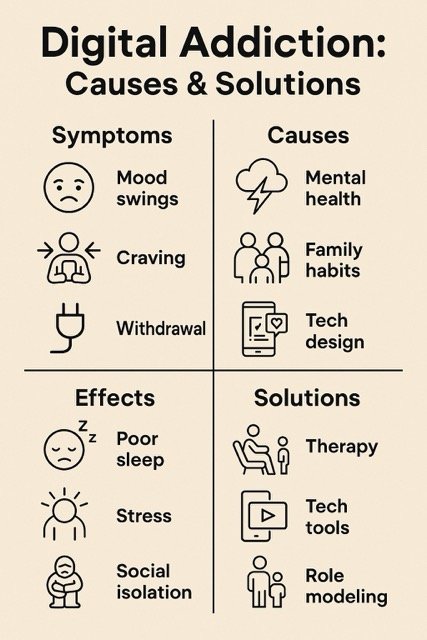
Conclusion
Digital addiction is a modern challenge—but it’s one we can overcome. By understanding its causes and effects, and by adopting practical strategies like therapy, tech boundaries, and family engagement, we can build healthier relationships with technology.




